-40%
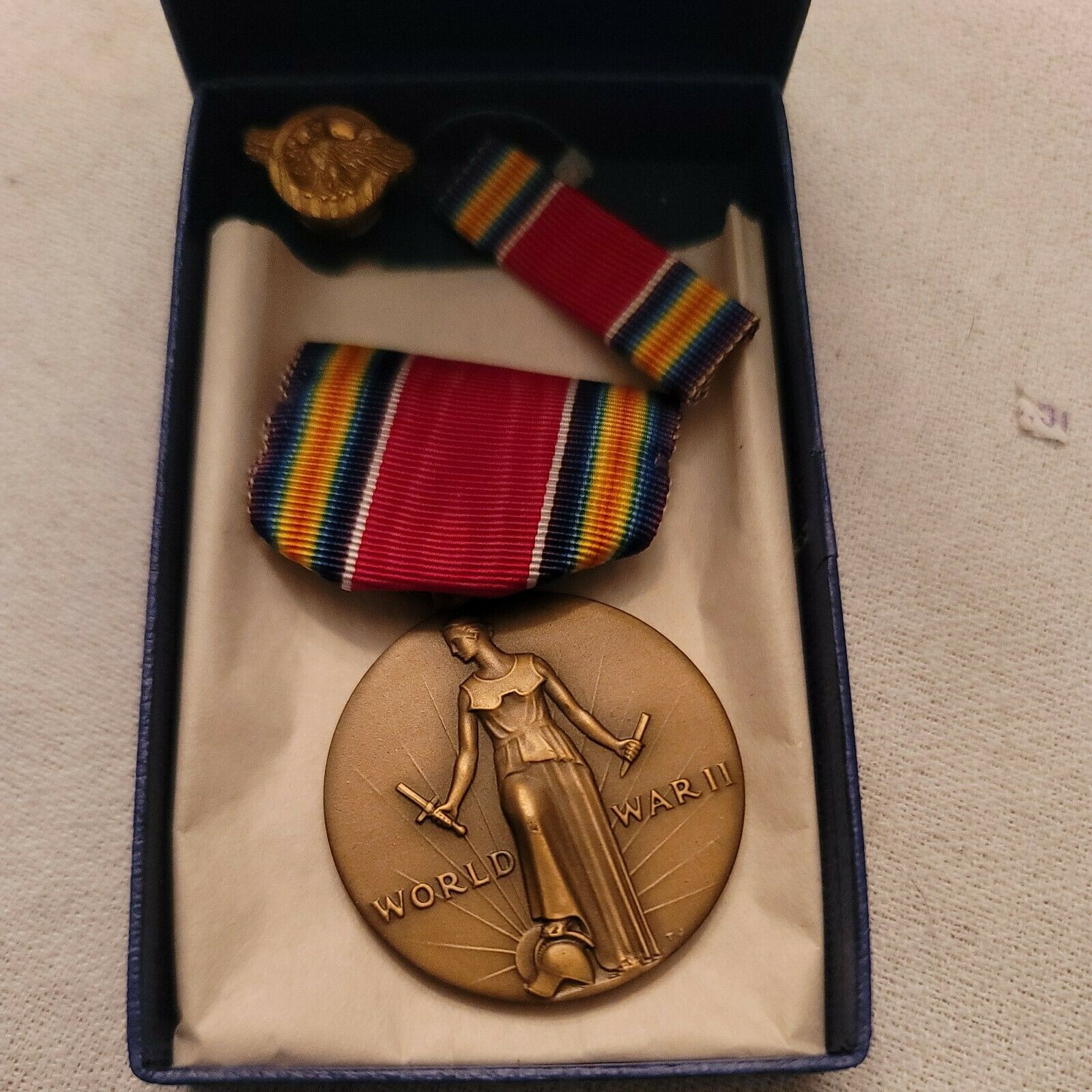
WW2 VICTORY MEDAL + RIBBON +ORIGINAL BOX DATED 1946 WITH RUPTURED DUCK BADGE
$ 10.55
- Description
- Size Guide
Description
WE SHIP WORLDWIDE 14 EUROPLEASE FOLLOW OUR E BAY STORE
SEE ALL PICS
WE COMBINE SHIPPING ( no shipping fee for the second item when you buy two or more like items )
SALE
SEE OUR STORE
PLEASE READ WHOLE ADD
VERY REAL THING
PLESE LOOK AT ALL PICS
RUPTURED DUCK BADGE MADE IN 1970s
#1# suggestions found. Use up and down keys to navigate
Honorable Service Lapel Button
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Honorable Service Lapel Button
The
Honorable Service Lapel Button,
sometimes called the
Honorable Service Lapel Pin,
was awarded to
United States
military service members who were discharged under honorable conditions during
World War II
.
[1]
The award is sometimes colloquially called the
Ruptured Duck
.
[2]
Sculptor
Anthony de Francisci
designed the award.
The Department of Defense awarded the button between September 1939 and December 1946, and it was made of gilt brass, except during metal shortages during which it was made of gilt plastic. Service members who received the plastic version were later allowed to trade it in for the brass version.
Design and wear
[
edit
]
The button is approximately 7/16 inch in height and 5/8 inch in width. A cloth
lozenge
depicting the gold colored button design was also issued. The lozenge was approximately 1.5 inches in height and 3 inches in width with the ring design being approximately 1 inch in diameter. Honorably discharged veterans wore the lapel pin on the left lapel of civilian clothing and the lozenge was sewn onto the right breast of the dress uniform that they wore when being discharged.
[1]
Even though the button depicts an eagle, the design of the eagle itself seems to depict its breast bursting through the button as though it has ruptured, and the eagle was believed by some to have been so poorly designed as to resemble a duck rather than an eagle; the term "ruptured duck" was coined to refer to it on that basis.
[
citation needed
]
Purpose
[
edit
]
The award served several purposes. It served as proof that the wearer was an honorably discharged veteran returning from duty. Unofficially, it was also used as an identifier to railroad, bus, and other transportation companies who offered free or subsidized transportation to returning veterans.
Honorable Discharge Emblem lozenge
During
World War II
, members of the armed forces were forbidden to possess civilian clothing unless they were under specific orders to do so. This not only made desertion more difficult, but also ensured that any captured service member would be treated as a prisoner of war under the rules of war. (Soldiers captured in combat zones in possession of civilian clothing were liable to be treated as spies and
summarily executed
.) In pre-war conditions, discharged veterans typically donned civilian clothing when returning home, but this was logistically difficult during wartime and immediate post-war America. Approximately 16 million men and women served in the uniformed services during the crisis, most of whom were scheduled to be discharged within a short period of time during the general demobilization at the end of the war. Clothing was already in short supply due to cloth
rationing
, and the immediate clothing needs of millions of returning veterans threatened to crash an already overtaxed system. Federal law, however, prevented civilians, even veterans, from wearing military uniforms under most circumstances. The Honorable Service Lapel Button was created to allow returning veterans to continue, legally, to wear their military uniforms while, at the same time, signifying that they had ceased to be active duty personnel.
The discharge insignia, embroidered onto a cloth
lozenge
and sewn on the right breast of the tunic, allowed its wearer to continue to wear his or her uniform for up to thirty days subsequent to discharge. Some veterans wore the pin on their civilian lapels for many years after the end of the war. It also appeared on a
postage stamp
honoring veterans, and is widely used as an unofficial symbol of veterans' pride.
The usage of the term "ruptured duck" later expanded to also refer to individuals wearing it, as in "that ruptured duck is flying
space-available
." Presumably because these individuals were usually in a great hurry to return to their homes in the United States, the term later came into use when describing somebody or something which was moving quickly
World War II Victory Medal
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
(Redirected from
World War II Victory Medal (United States)
)
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
For the medal awarded to merchant mariners, see
Merchant Marine World War II Victory Medal
.
World War II Victory Medal
World War II Victory Medal
Type
Military service medal
Presented by
Department of War
and
Department of the Navy
Eligibility
Served in the armed forces between the dates of 7 December 1941 and 31 December 1946.
Status
Retired
Service ribbon
(top) and
campaign streamer
(bottom)
Precedence
Next (higher)
European-African-Middle Eastern Campaign Medal
Equivalent
Merchant Marine World War II Victory Medal
Next (lower)
Army of Occupation Medal
or
Navy Occupation Service Medal
The
World War II Victory Medal
is a
service medal
of the
United States military
which was established by an Act of
Congress
on 6 July 1945 (Public Law 135, 79th Congress) and promulgated by Section V, War Department Bulletin 12, 1945.
[1]
[2]
The
World War I Victory Medal
is the corresponding medal from
World War I
.
The World War II Victory Medal was first issued as a
service ribbon
referred to as the “Victory Ribbon.” The World War II Victory Medal was established by an Act of Congress on 6 July 1945 (Public Law 135, 79th Congress) and promulgated by Section V, War Department Bulletin 12, 1945. The medal was designed by Mr. Thomas H. Jones and approved by the Secretary of War on 5 February 1946. Consequently, it did not transition from a ribbon to a full medal until after
World War II
had ended.
The Congressional authorization for the medal specified that it was to be awarded to any member of the United States military, including members of the armed forces of the
Government of the Philippine Islands
, who served on active duty, or as a reservist, between 7 December 1941 and 31 December 1946.
[2]
On 8 August 1946, the separate
Merchant Marine World War II Victory Medal
was established for members of the
United States Merchant Marine
who served during World War II.
[3]
Criteria
[
edit
]
The World War II Victory Medal was awarded for service between 7 December 1941 and 31 December 1946, both dates inclusive, with no minimum time in service requirement.
[1]
The
National Personnel Records Center
has reported some cases of service members receiving the award for only a few days of service. As hostilities during the Second World War ended on 2 September 1945, there may be cases of service members who had enlisted, entered officer candidate school, or had been a cadet or midshipman at the
U.S. Military Academy
, the
U.S. Naval Academy
or the
U.S. Coast Guard Academy
between 3 September 1945 and any date in 1946, receiving the medal without having been a veteran of World War II itself. The reason for this late date is that President
Harry S. Truman
did not declare an official end to hostilities until the last day of 1946.
[2]
As every member of the United States Armed Forces who served from 7 December 1941 to 31 December 1946 was eligible for the medal, there were over 12 million eligible recipients, making the World War II Victory Medal the second most widely awarded military award of the United States, after the
National Defense Service Medal
.
[4]
[5]
Appearance
[
edit
]
The bronze medal is 1
1
⁄
2
inches in width. The
obverse
is a figure of Liberation standing full length with head turned to dexter looking to the dawn of a new day, right foot resting on a war god’s helmet with the hilt of a broken sword in the right hand and the broken blade in the left hand, the inscription
WORLD WAR II
placed immediately below the center. On the
reverse
are inscriptions for the
Four Freedoms
:
FREEDOM FROM FEAR AND WANT
and
FREEDOM OF SPEECH AND RELIGION
separated by a palm branch, all within a circle composed of the words
UNITED STATES OF AMERICA 1941 1945
.
[2]
The suspension and
service ribbon
of the medal is 1
3
⁄
8
inches wide and consists of the following stripes:
3
⁄
8
inch double rainbow in juxtaposition (blues, greens, yellows, reds (center), yellows greens and blues);
1
⁄
32
inch White 67101; center
9
⁄
16
inch Old Glory Red 67156;
1
⁄
32
inch White; and
3
⁄
8
inch double rainbow in juxtaposition. The rainbow on each side of the ribbon is a miniature of the pattern used in the
World War I Victory Medal
.
[2]
The
National World War II Memorial
has an engraving of it in one of the two pavilions